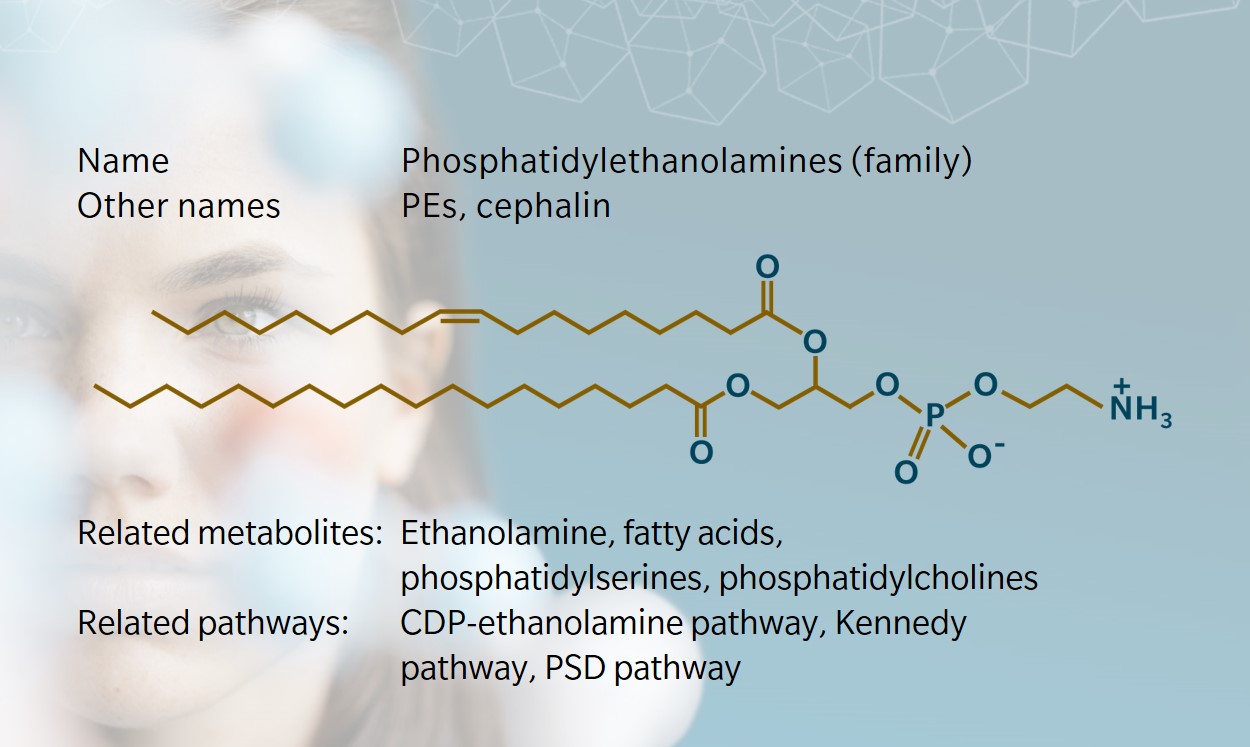
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is a sub-class of phospholipids with a variety of functions in animals, plants and microorganisms. Like other phospholipids, PEs are more than simply the building blocks of membranes
All posts to the category
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the liver. This organ is responsible for a variety of important functions, including filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile, and storing glucose. In several pathologies, the liver can also be the place of large fat storage associated with metabolic diseases.
Metabolic effects of anti-TNF α therapy
Anti-TNF α therapy in Crohn´s Disease improves liver steatosis through changes in gut bacteria and triglycerides.
Metabolism of fatty liver disease and the impact of therapy
New study demonstrates the power of metabolomics in boosting our understanding of fatty liver disease – and possible treatments. Obeticholic acid reverses metabolic changes in NASH.
Elevated liver fat content disrupts the liver-α cell axis
Elevated liver fat is related to hyperglucagonaemia, which reflects the disruption of the liver-α cell axis.
Prenatal PFAS exposure leads to liver injuries in children
HELIX metabolomics study links prenatal PFAS (perfluoralkyl substances) exposure to metabolic origin of liver injuries in children.