Acylcarnitine assay


Acylcarnitine assay
Understand energy homeostasis across generations
Acylcarnitines play an exceptional role in the understanding and diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism. A growing body of evidence puts acylcarnitines now in the spotlight of uncovering mechanisms of aging and age-related diseases. Acylcarnitines and their regulation are the missing piece between cellular malfunction and physiological outcome – a set of universal markers for energy homeostasis across generations.
Understand energy homeostasis across generations
Acylcarnitines play a vital role in energy production and metabolism. Studying them can help us understand and diagnose inborn errors of metabolism and explore mechanisms of aging and age-related diseases. Acylcarnitines are the missing link between cellular malfunction and physiological outcome – a set of universal markers for energy homeostasis across generations.
Comprehensive coverage
- Increased acylcarnitine panel beyond usual clinical coverage to discover new markers
- Relevant metabolite sums and ratios to better understand enzyme activities and regulations

Clinical applications
- Novel applications in diseases such as cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease
- Screening for inborn errors of metabolism

Reliable and reproducible
- Results can be combined with other biocrates kit or assay results to maximize insights
- Comprehensive, quantitative data supports biomarkers and therapeutic target studies

Understand the implications
- Support in data interpretation available
- Tools to translate metabolomics into knowledge
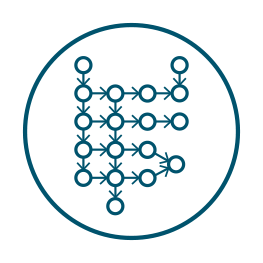
Acylcarnitines in health and disease
Analysis of acylcarnitines is a go-to check when screening blood for inborn errors of metabolism. There is also growing interest in how acylcarnitines can help to understand and diagnose other metabolic diseases, such as certain types of cancer, cardiovascular diseases and neurological disorders.
Many diseases are associated with changes in acylcarnitine metabolism
- Alzheimer´s disease
- Depression
- Hepatocellular cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Liver disease (NASH)
- Newborn screening
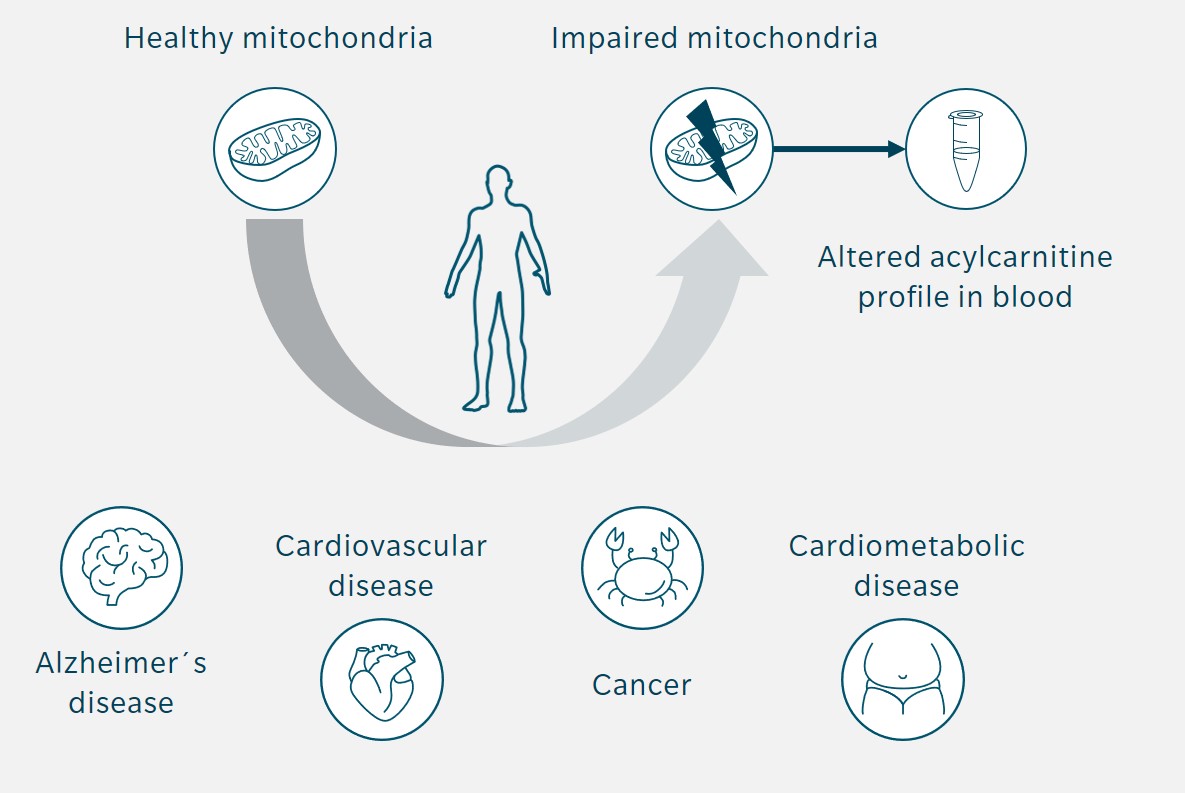
Role of acylcarnitines in cellular and systemic metabolism
Acylcarnitines’ role in both, glucose and fatty acid metabolism
- Regulate beta-oxidation
- Maintain the balance between beta-oxidation and glucose oxidation
- Involved in metabolism of branched chain amino acids (BCAA)
- Involved in production of ketone bodies
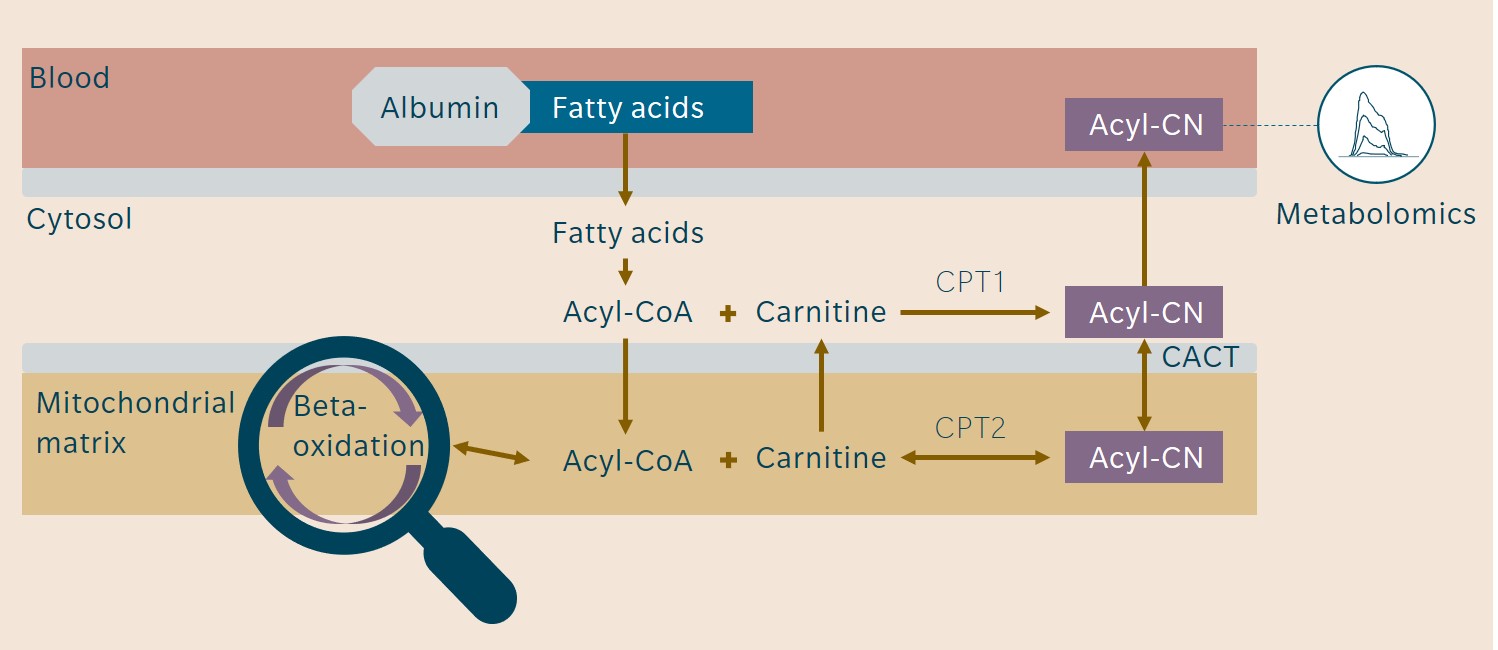
How to read mitochondrial metabolism from plasma.
More Resources
biocrates blog articles and insights from the literature
Metabolite of the month is your sneak peek into the world of metabolomics. This month we look at carnitine #loveyourmetabolites
The metabolic cost of a marathon: fitness matters
Targeted metabolomics reveals differences in metabolic profiles between top athletes and amateur runners days after running a marathon.
Relevant Literature
- Metabolic network failures in Alzheimer’s disease – A biochemical road map
Toledo et al., Alzheimers Dement 2017 - Simplified plasma essential amino acid-based profiling provides metabolic information and prognostic value additive to traditional risk factors in heart failure
Wang et al., Amino Acids 2018 - Mitochondrial dysfunction-related lipid changes occur in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression
Peng et al. J. Lipid Res. 2018 - Comprehensive Metabolomic Search for Biomarkers to Differentiate Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Cirrhosis
Kim et al. Cancers (Basel) 2019
For research use only | not for use in diagnostic procedures.